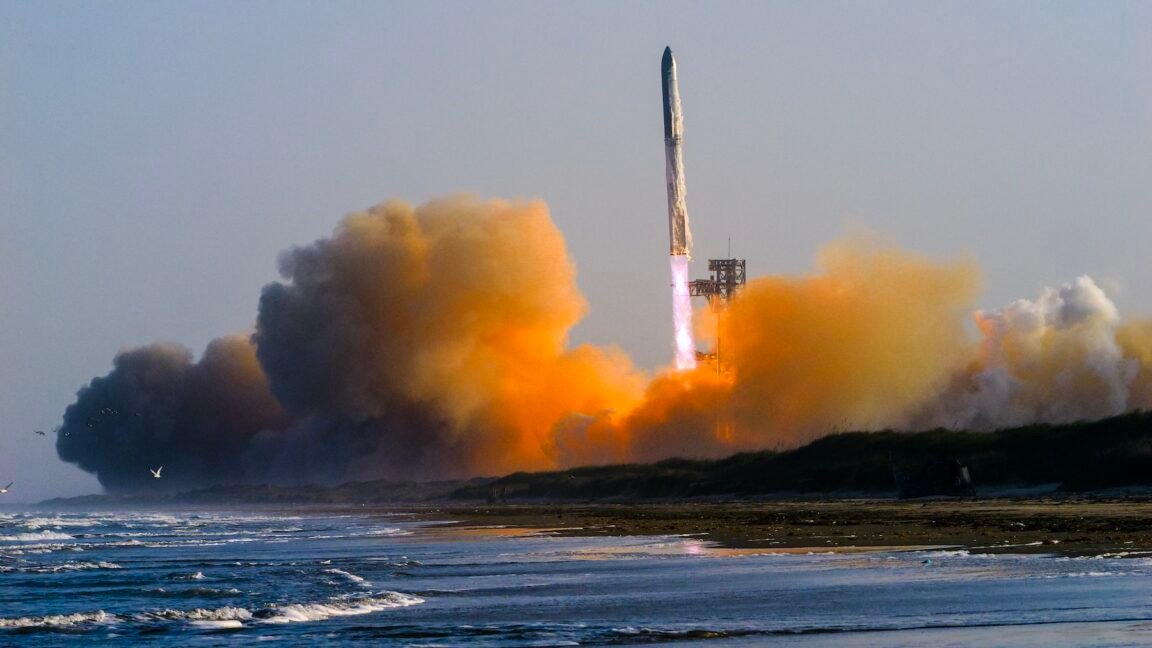
“This is all happening really fast,” said Victoria Samson, chief director of space security and stability for Secure World Foundation, in an interview.
Crowded orbits
Samson said that, at present, satellites have a fairly large “bubble” of space around them when it comes to collision detection. This is because of uncertainties in the precise location and movement of vehicles. If you improve space situational awareness, such as what SpaceX seeks to do with Stargaze, those bubbles could be shrunk to reduce the number of potential collision warnings. But that will come with risks.
“There’s a lot of room in space, of course,” Samson said. “But the question is, how much risk do you want to take?”
A technical expert at The Aerospace Corporation, Marlon Sorge, told Ars that many unanswered questions about SpaceX’s proposed megaconstellation for orbital data centers make it difficult to assess the risks of collision. This includes their size (they will require very large solar arrays to collect sunlight) and precisely where the satellites will be deployed. There is already a lot of debris at around 800 to 1,000 km above Earth from previous collisions, including from an infamous Chinese anti-satellite missile test in 2007, which created more than 3,000 pieces of golf-ball-sized or larger debris.
Above that altitude, there is less debris, Sorge said. But objects at that altitude take centuries to deorbit naturally, due to the very limited atmosphere.
“The big challenge at those altitudes is the stuff that’s up there stays up there,” Sorge said. “If you generate more debris, if you have problems, it won’t go away, so you’re stuck with it.”
SpaceX sought to address these concerns in its regulatory filing, noting that each satellite would have “redundant maneuverability capabilities” in order to deorbit into Earth’s atmosphere. The filing also appears to recognize emerging science that indicates that aluminum burning up from reentering satellites is harmful to ozone levels. To address this, SpaceX is considering moving aging satellites into “high altitude Earth orbits or heliocentric orbits.”